4 Types of Gear Failure to Watch Out For
Introduction
At PairGears, we understand that gears are fundamental components in a wide range of industrial applications, from agricultural machinery to heavy-duty trucks. Our gear systems are meticulously engineered to ensure performance and durability. However, even the best-designed gears can suffer from various types of failures if not properly maintained or if they operate under suboptimal conditions.
In this blog, we’ll discuss the four most common types of gear failure you should watch out for. Understanding these failures, their causes, and how to prevent them will help you ensure the longevity and reliability of your gear systems.

1. Gear Tooth Wear
Gear Tooth Wear is one of the most common types of gear failure. It occurs when the surface of the gear teeth wears down due to continuous friction during operation. Over time, this can lead to reduced tooth contact and gear slippage.
Causes:
• Inadequate lubrication: Lack of lubrication leads to metal-to-metal contact, which causes friction and wear.
• Improper alignment: Misalignment of gears can cause uneven pressure distribution, resulting in excessive wear on the teeth.
• Overloading: Operating gears beyond their designed capacity can accelerate tooth wear.
Prevention:
• Regular lubrication with high-quality gear oils helps reduce friction.(Gear Lubrication Methods: Benefits and Oil Types)
• Ensuring proper alignment during installation and regularly checking for misalignment can prevent uneven wear.
• Implementing load monitoring systems to avoid overloading gears.
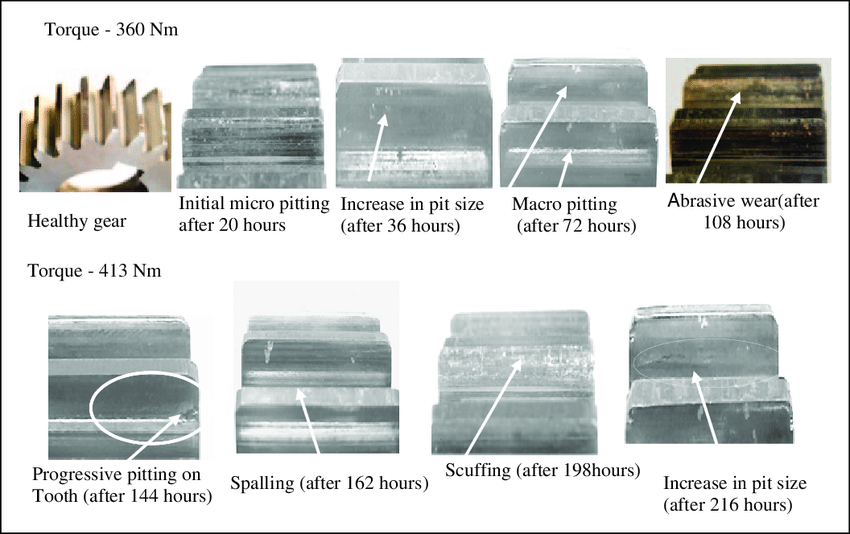
2. Pitting and Scuffing
Pitting refers to the formation of small pits or cavities on the surface of gear teeth, often due to the initiation of fatigue. Scuffing, on the other hand, occurs when the friction between the teeth is so intense that it leads to the tearing of the surface material.
Causes:
• Excessive pressure or heat: When gears operate at high temperatures or under high loads, the material can begin to degrade, leading to pitting and scuffing.
• Inadequate lubrication: Without proper lubrication, friction increases significantly, leading to these forms of surface damage.
Prevention:
• Using high-quality lubricants that can withstand high pressures and temperatures.
• Reducing the operational load to within the manufacturer's specifications can help avoid excessive pressure on the gear teeth.
• Regular maintenance to check for signs of wear and replace damaged gears promptly.

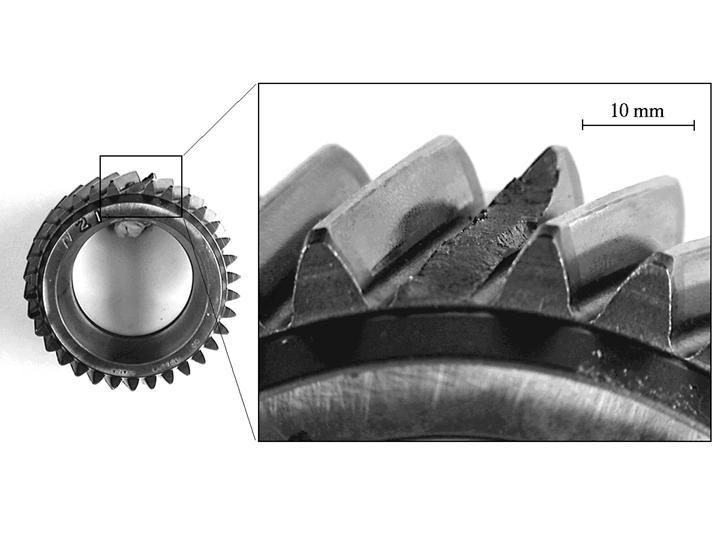
3. Tooth Fracture
Tooth fractures are serious gear failures where the teeth of the gear break or crack under stress. This type of failure can result in catastrophic damage to the gear and the entire system.
Causes:
• Overloading: Subjecting the gears to loads that exceed their design specifications can cause the teeth to crack or break.
• Fatigue stress: Continuous repetitive stress on the gears, especially in high-speed applications, can lead to micro-cracks forming on the tooth surface, eventually causing fractures.
Prevention:
• Ensuring that gears operate within the recommended load limits and speeds. Regular checks for overloading should be performed.
• Using gears made from high-strength materials or applying surface treatments such as induction hardening (explore our high-quality gears at PairGears here) can help resist fatigue.
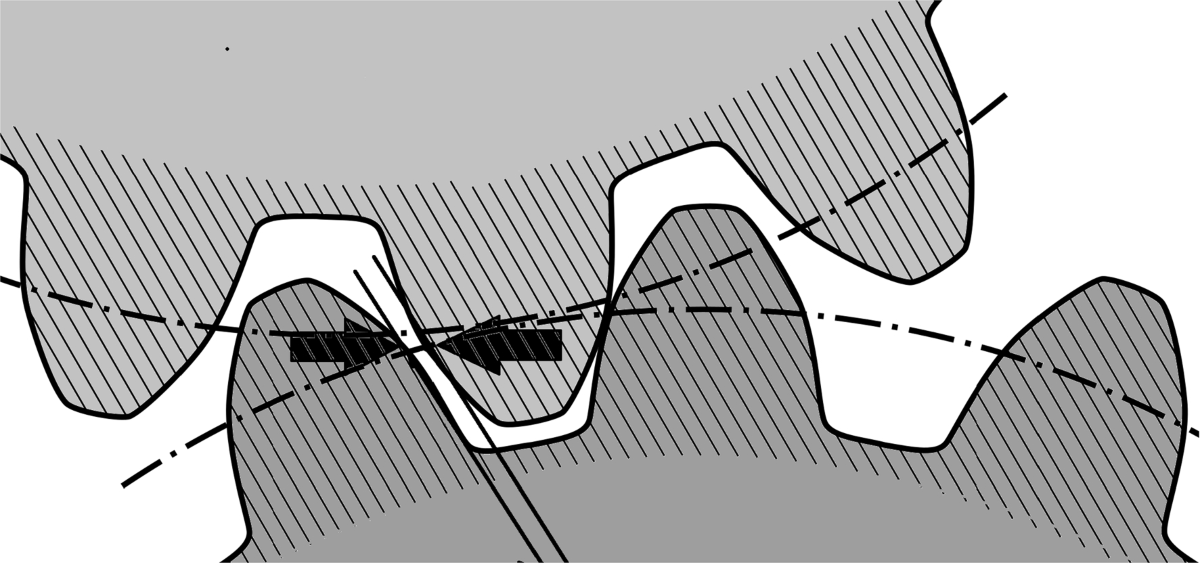
4. Gear Backlash
Backlash is the amount of play or movement between the gear teeth when the direction of motion is reversed. While a small amount of backlash is typically allowed, excessive backlash can lead to inaccurate performance, increased wear, and even failure.I wrote a blog about gear backlash before, you can click to browse if you are interested.
Causes:
• Improper installation: If the gears are not properly meshed during installation, excessive backlash can occur.
• Wear and tear: Over time, as gears wear down, the teeth may become loose, leading to an increase in backlash.
Prevention:
• Regularly inspect gears for any signs of looseness or excessive movement.
• Ensure gears are properly installed with the correct clearance and meshing.
How to Prevent Gear Failures
Preventing gear failure is a combination of selecting the right materials(Choosing the Right Material for Gears: An Overview), proper maintenance, and correct installation. Here are a few key steps that can help prolong the life of your gear systems:
• Choose high-quality materials: Using durable, high-strength materials for gears can prevent many types of failures. For example, gears made from bronze or alloy steel offer enhanced durability.
• Regular maintenance: Implementing a preventive maintenance program that includes checking lubrication, alignment, and wear can help detect issues before they lead to failure.
• Load management: Ensuring that your gears operate within their specified load limits will prevent issues such as tooth fractures and pitting.
At PairGears, we manufacture high-quality gears designed for durability and long-lasting performance. Our products are suitable for a wide range of industries, including agriculture, automotive, and heavy-duty machinery.
Conclusion
Gear failures can be costly and disruptive, but with proper care and attention to detail, many of these issues can be avoided. Understanding the common causes of gear failure, such as tooth wear, pitting, fractures, and backlash, allows you to take proactive measures to protect your gear systems. Regular maintenance, proper installation, and selecting the right materials are essential for keeping your gears in top condition.
If you’re looking for high-performance gears for your machinery, PairGears offers an extensive range of gear solutions designed for maximum efficiency and durability. For more information, visit our website and contact us today!
Should you have any questions or require further assistance, please do not hesitate to contact our engineer: ben@pairgears.com.








