Gear Milling Process Explained
Introduction to Gear Milling
Gear milling is a machining process used to create gear teeth on a cylindrical or conical surface using a milling machine. It plays an essential role in producing gears that are critical for mechanical systems, ranging from agricultural machinery to industrial equipment. At PairGears (www.pairgears.com), we use advanced gear milling technologies to ensure precision and durability in our gear products.
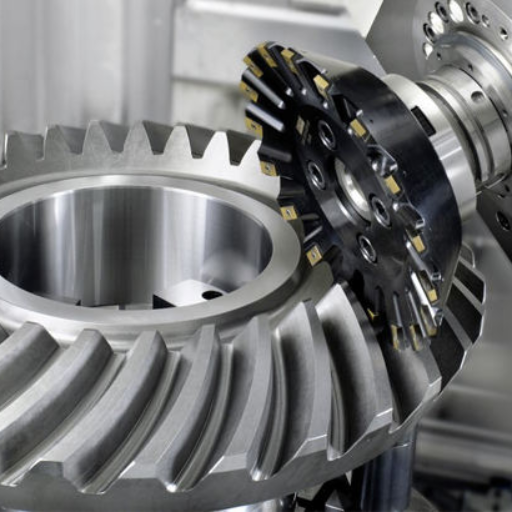

How Gear Milling Works
Gear milling involves the removal of material from a blank to form gear teeth. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
1. Preparation of the Gear Blank: The blank is made from materials like alloy steel, carbon steel, or cast iron, depending on the application.
2. Mounting on the Milling Machine: The blank is securely mounted on the machine.
3. Selection of the Cutter: Specialized gear milling cutters, such as form cutters or indexable cutters, are used.
4. Gear Cutting: The cutter is rotated at high speeds to create the desired tooth profile, typically an involute or cycloidal shape.
5. Finishing: Post-milling processes like grinding and surface treatment enhance the gear's performance.
Types of Gear Milling Techniques
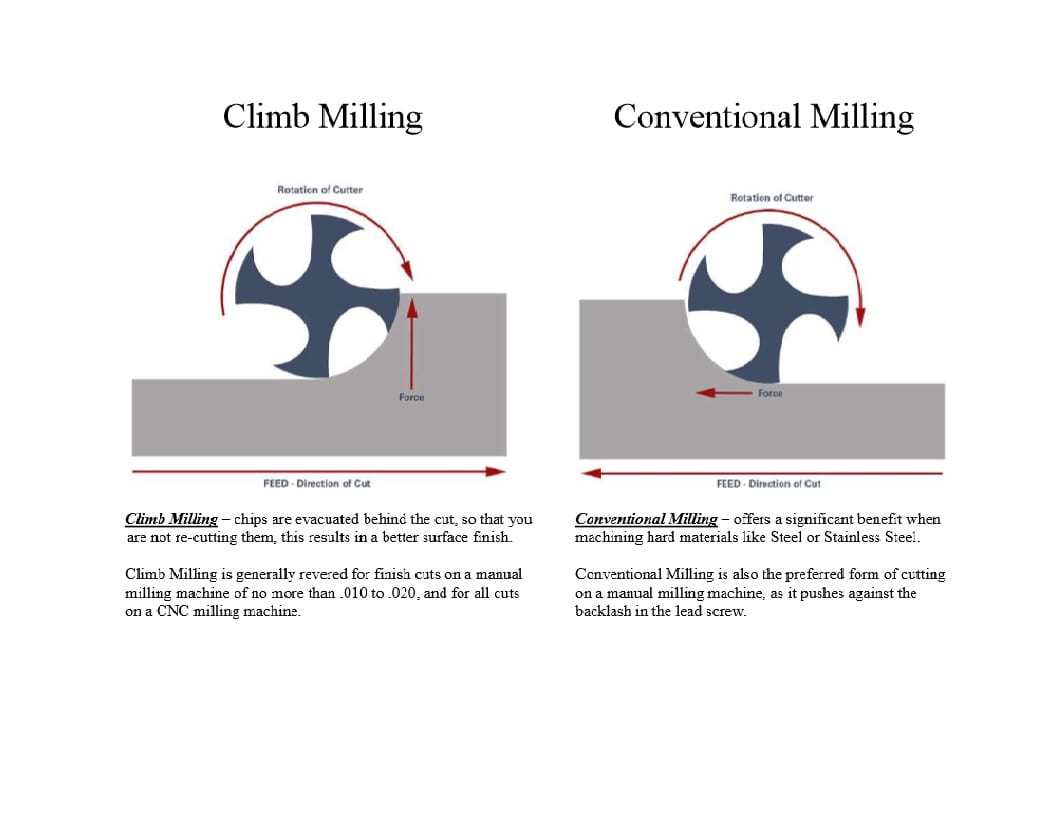
1. Conventional Milling:
· Chip width starts from zero and increases which causes more heat to diffuse into the workpiece and produces work hardening
· Tool rubs more at the beginning of the cut causing faster tool wear and decreases tool life
· Chips are carried upward by the tooth and fall in front of cutter creating a marred finish and re-cutting of chips
· Upwards forces created in horizontal milling tend to lift the workpiece, more intricate and expansive work holdings are needed to lessen the lift created
2. Climb Milling:
· Chip width starts from maximum and decreases so heat generated will more likely transfer to the chip
· Creates cleaner shear plane which causes the tool to rub less and increases tool life
· Chips are removed behind the cutter which reduces the chance of re-cutting
· Downwards forces in horizontal milling are created that help hold the workpiece down — less complex work holdings are need when coupled with these forces
Advantages of Gear Milling
1. High Precision: Achieves tight tolerances and complex designs.
2. Versatility: Suitable for various gear types, such as spur gears, helical gears, and bevel gears.
3. Cost-Effectiveness: High production efficiency reduces costs for large-scale manufacturing.
Why Choose PairGears?
At PairGears, we excel in manufacturing custom gears using state-of-the-art gear milling techniques. Our team ensures:
1. Strict Quality Control: Every gear undergoes rigorous testing.
2. Tailored Solutions: Customization based on client specifications.
3. Global Reach: Trusted by industries across Europe, North America, and South America.
Learn more about our custom gear services here.
Conclusion
Gear milling is a cornerstone of modern gear manufacturing, combining precision and efficiency to produce high-quality gears. At PairGears, we are committed to delivering top-notch gear products that meet the diverse needs of industries worldwide. Contact us today to learn how our expertise in gear milling can support your business.
Should you have any questions or require further assistance, please do not hesitate to contact our engineer: ben@pairgears.com.
